Turbid Water Can Be Treated By Settling Out Sediment. This Process Also Removes Some Pathogens
Turbid water can be treated by settling out sediment. This process also removes some pathogens.
Note: The content on this page has been adapted from publications of World Health Organization (WHO) and Centre for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST).
How Does Sedimentation Work?
Sedimentation is the process of removing sediment from turbid water.
Let a container of water sit without moving for 24 hours and then pour the clear water into a clean container. This process can be repeated 2 to 3 times as needed.
Effectiveness
* Quality: Somewhat effective for removing turbidity and some pathogens
* Quantity: Depends on the size of container being used
* Local water: Can be used with any water source
Appropriateness
* Local availability: Can use any container
* Time: 24 hours
* Operation and maintenance: Simple; need to wash container afterwards
* Lifespan: Containers may need to be replaced
Acceptability
* Taste, smell, color: May be improved
* Ease of use: Very easy
Cost
* Initial purchase cost: Free or low cost since households can use any container
* Operating cost: None
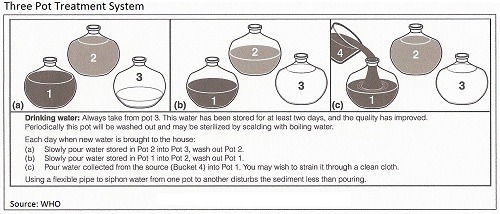
A household can maximize the benefit of sedimentation by using the three-pot system shown in the illustration.
How Does Chemical Coagulation Work?
The sedimentation process can be quickened by adding special chemicals, also known as coagulants, to the water. Coagulants help the sand, silt, and clay join together and form larger clumps, making it easier for them to settle to the bottom of the container.
Three common chemicals used for cleaning turbid water are aluminum sulphate, polyaluminum chloride (also known as PAC or liquid alum) and ferric sulphate.
Effectiveness
* Quality: Somewhat effective for removing turbidity and some pathogens; varies depending on the water
* Quantity: Depends on the size of container being used
* Local water: Can be used with any water source
Appropriateness
* Local availability: Chemical coagulants are not always available; can use any container
* Time: 2+ hours
* Operation and maintenance: Follow manufacturer's instructions for specific products; need to wash container afterwards
* Lifespan: 6 months in liquid form and 1 year in solid form; containers may need to be replaced
Acceptability
* Taste, smell, color: May be improved
* Ease of use: Follow manufacturer's instructions for specific products
Cost
* Initial purchase cost: None
* Operating cost: On-going cost to buy chemical coagulants as they are used
How Do Natural Coagulants Work?
The sedimentation process can be quickened by adding natural coagulants to the water. Coagulants help the sand, silt and clay join together and form larger clumps, making it easier for them to settle to the bottom of the container.
There are a variety of natural products which have been used in Africa and Latin America to help with sedimentation and cleaning turbid water, including movings seeds, prickly pear and lava beans.
Effectiveness
* Quality: Somewhat effective for removing turbidity and some pathogens; varies depending on the water
* Quantity: Depends on the size of container being used
* Local water: Can be used with any water source
Appropriateness
* Local availability: Natural coagulants are not always available; can use any container
* Time: 2+ hours
* Operation and maintenance: Need to dry and grind seeds before adding them to water; need to wash container afterwards
* Lifespan: Dried beans and seeds can be stored for a long time; prickly pear cactus needs to be used before the sap dries; containers may need to be replaced
Acceptability
* Taste, smell, color: May improve color; may cause an objectionable taste
* Ease of use: Need to prepare natural coagulants beforehand; easy to add coagulants to water
Cost
* Initial purchase cost: None
* Operating cost: None
Return to "Water Treatment" from "Turbid Water
Return "Home"